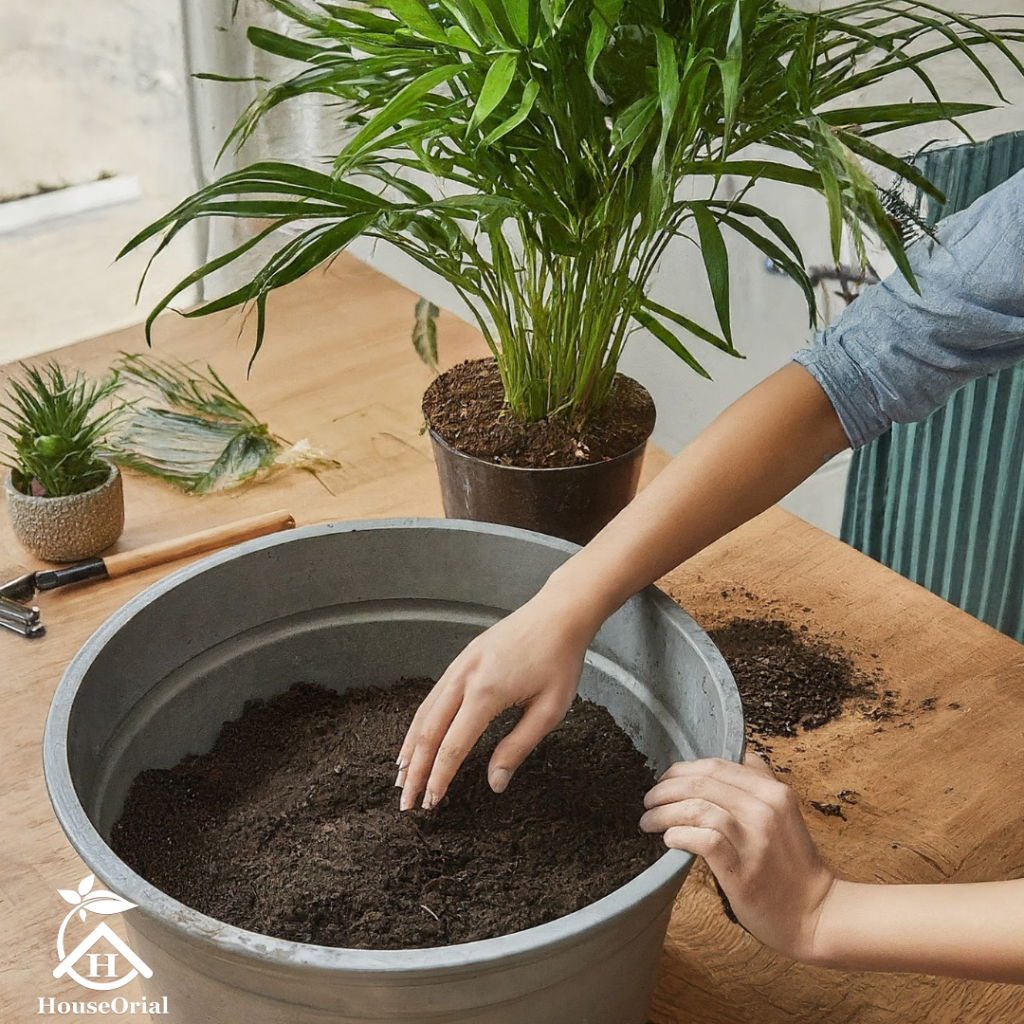
When it comes to indoor gardening, one of the most common questions that arises is, “Can I use outdoor soil for indoor plants?” Choosing the right soil is crucial for the health and growth of your plants, as it provides essential nutrients and support. In this blog post, we’ll explore whether outdoor soil is a suitable option for your indoor garden, weigh the pros and cons, and share expert tips to help you decide what’s best for your green space.

Table of Contents
Understanding Soil Composition for Indoor Gardening
To determine if outdoor soil can be used indoors, it’s important to understand the differences between outdoor soil and indoor potting mix.
What Makes Up Outdoor Soil?
Outdoor soil is a complex mix of minerals, organic matter, microorganisms, and more. It typically contains:
- Sand, silt, and clay: These particles affect soil texture and drainage.
- Organic matter: decayed plant and animal material that provides nutrients.
- Microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that contribute to soil health.
What’s Inside an Indoor Potting Mix?
Indoor potting mixes are specially formulated to meet the needs of potted plants. They often include:
- Peat moss or coco coir: lightweight materials that retain moisture and improve aeration.
- Perlite or vermiculite: minerals that enhance drainage and aeration.
- Compost: organic material that supplies nutrients.
- Fertilizers: added nutrients to support plant growth.
Differences between outdoor and indoor soil
- Drainage problems: Outdoor soil tends to be heavy and compacted, which lacks the aeration and drainage needed by container plants. This can result in waterlogging, suffocation of roots, and the invitation of fungal diseases such as root rot. Indoor potting mixes, on the other hand, are light and fluffy, able to retain moisture, and ideal for good drainage and waterlogging prevention.
Read More: 20 Fastest Growing Vegetables Indoors in 20-30 Days
16 Toxic House plants to Humans That Can Cause Serious Harm
Top 20 Small plants that don’t need sunlight
Can I grow vegetables indoors? – 10 Tips for Successful!
How to Plant Seeds Indoors
What the Experts Say
Dr. Linda Chalker-Scott, a horticulturist at Washington State University, emphasizes the importance of proper drainage for container plants. “[Outdoor soil] can become compacted and doesn’t allow for good drainage, which can lead to root rot,” she says. [Source: WSU Extension Gardener]
- Pest Party Crashers: Outdoor soil can harbor unwanted guests—weed seeds, insect larvae, and even pathogens. Bringing these hitchhikers indoors can infest your plants and potentially spread to other houseplants. On the other hand, potting mixes are usually sterilized to avoid pests and diseases, unlike outdoor soil.
- Nutrient Imbalance: The nutrient content of outdoor soil can vary greatly depending on your location and past plantings. It might be lacking in essential nutrients that indoor plants require for healthy growth or, conversely, contain an excess that can harm them. Indoor mixes, on the other hand, are often enriched with nutrients made for container plants.
Pros and Cons of Using Outdoor Soil for Indoor Plants
Benefits of Outdoor Soil
- Cost-effective: Using soil from your garden is free.
- Natural composition: Contains a diverse range of microorganisms and organic matter.
Drawbacks of Outdoor Soil for Indoor Plants
- Pests and diseases: Outdoor soil can bring insects, fungi, and bacteria indoors.
- Poor drainage: Can lead to waterlogged roots and root rot.
- Soil compaction: Outdoor soil tends to compact more in containers, restricting root growth.
Potential Risks of Using Outdoor Soil for Indoor plants
Using outdoor soil indoors carries several risks that can affect your plants’ health.
Pests and Diseases
Outdoor soil is home to many organisms, some of which can be harmful to indoor plants. These include:
- Insects: Aphids, ants, and other pests can infest indoor plants.
- Fungal infections: Soil-borne fungi can cause diseases like damping-off.
- Bacteria: Harmful bacteria can spread and affect plant health.
Soil Compaction and Drainage Issues
- Compaction: Outdoor soil can become compacted in pots, reducing aeration and root growth.
- Poor Drainage: Without proper drainage, water can accumulate, leading to root rot.
Nutrient Imbalance
- Nutrient Deficiency: Outdoor soil might not provide the balanced nutrients indoor plants need.
- Over-fertilization: Adding too much fertilizer to compensate can harm plants.
How to Prepare Outdoor Soil for Indoor Plants
If you decide to use outdoor soil, there are steps you can take to make it more suitable for indoor plants.
Sterilizing the Soil
- Heat Treatment: Bake soil in the oven at 180°F for 30 minutes to kill pests and pathogens.
- Solarization: Place soil in clear plastic bags and leave it in the sun for several weeks.
Improving Soil Texture and Drainage
- Add Perlite or Sand: Mix in perlite or sand to enhance drainage.
- Include Organic Matter: Add compost or peat moss to improve soil structure and nutrient content.
Adding Nutrients
- Balanced Fertilizer: Incorporate a balanced fertilizer to ensure plants get the nutrients they need.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Use slow-release fertilizers for steady nutrient supply.
Alternative Solutions
If using outdoor soil seems too risky or labor-intensive, consider these alternatives.
Using Commercial Potting Mix
- Convenience: Ready-to-use and formulated for indoor plants.
- Sterility: Free from pests and diseases.
Making Your Own Potting Mix
- Customization: Tailor the mix to your plants’ specific needs.
- Basic Recipe: Combine equal parts peat moss, perlite, and compost.
Combining Outdoor Soil with Potting Mix
- Hybrid Approach: Mix outdoor soil with potting mix to balance cost and benefits.
- Proportion: Use a higher ratio of potting mix to outdoor soil (e.g., 3:1).
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Pitfall 1: Overlooking pest control.
- Solution: Always sterilize soil.
- Pitfall 2: Ignoring drainage.
- Solution: Ensure containers have drainage holes and add perlite to the soil mix.
Indoor Gardening: Best Practices You Should Know
- Regular Monitoring: Check plants regularly for signs of pests or diseases.
- Proper Watering: Avoid overwatering by allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between watering’s.
- Lighting: Ensure plants receive adequate light, whether natural or artificial.
Conclusion
Can I use outdoor soil for indoor plants? Using outdoor soil for indoor plants is a topic that garners much debate among gardening enthusiasts. While it is possible, it comes with its own set of challenges and risks. By understanding the differences between outdoor soil and indoor potting mix, preparing the soil properly, and considering alternative solutions, you can make an informed decision that best suits your indoor gardening needs.
Remember, successful indoor gardening is all about experimenting, learning, and creating a healthy environment for your plants. Happy gardening!